With thousands of potential allergens in the environment, it is not surprising that allergies are common. When allergies affect the skin and do not seem to go away with time or at-home treatments, you can turn to a licensed dermatologist for dermal allergy patch testing to uncover the problem.
Skin allergies affect more than 24 million people in the U.S. It is common among children but tends to go away on its own as they get older. A common skin allergy in infants and children is eczema. Nearly 20% of children show signs of it before they turn six months old.
Symptoms of skin allergies
Skin allergies are caused when your immune system reacts to a foreign substance or allergen. When your body does not recognize what it was exposed to, it releases antibodies to fight it off, which can result in allergy symptoms that range from mild to severe, including:
- Redness
- Rash
- Itching
- Burning
- Scaly patches
- Bumps
- Blisters
- Swelling
- Tenderness
Skin allergies can be difficult to prevent without knowing the cause of irritation. Dermal allergy patch testing is a diagnostic procedure performed by a dermatologist that can uncover the cause of the allergy.
It is effective for both children and adults. Allergy patch testing is a popular method of allergy diagnosis because of its non-invasive application and accuracy in identifying the exact cause of an allergic reaction.
Should I try patch testing?
Dermal patch allergy testing does not treat or cure a skin allergy. It is used as a tool to provide an understanding of your allergy triggers, but there are many advantages.
It is a simple and non-invasive test that is safe for children and adults. It can provide valuable information related to specific skin allergies for a wide range of allergens. Testing can help rule out other types of dermatological conditions once the cause of a rash is known.
The only risk associated with patch testing is the potential for mild skin irritation at the test areas. In rare cases, the patches will cause a severe allergic reaction. If this occurs, testing will be discontinued immediately.
How does patch testing work?
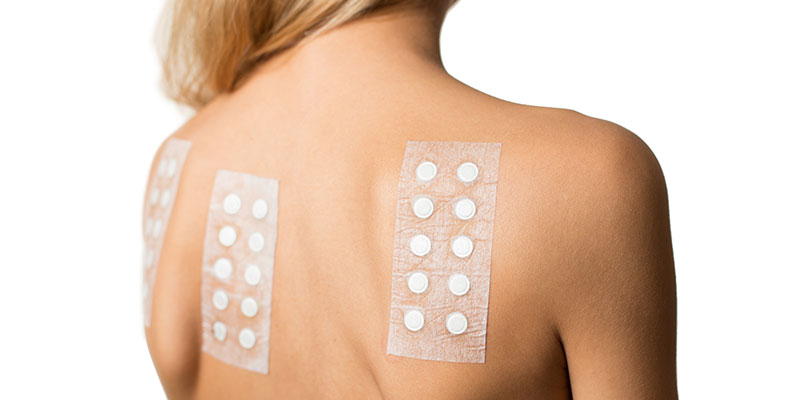
A dermatologist performs a patch test after a skin examination. Your physician will then place 25 or more small patches on the skin, usually on the upper back. The patches are secured with hypoallergenic tape and contain substances known to cause skin reactions or irritation. Common irritants include:
- Wool
- Latex
- Nickle
- Plants
- Resins
- Dyes
- Cosmetic additives
- Fragrances
The patches will remain on your skin for 48 hours, so you will need to keep the area dry and protected from the sun. Avoid exercising or any other sweat-inducing activity.
It is rare to have a severe side effect from a dermal allergy patch testing, but if you do experience reactions such as swelling, nausea, vomiting or difficulty breathing, get medical care immediately.
After two days, you return to have the patches removed. The dermatologist will examine the patched areas and identify any inflammation or breakouts.
What do patch test results look like?
If you have a reaction in one or more of the patched areas, your dermatologist can identify the specific substance causing the reaction. Common reactions are red spots, hives, burning sensation, blisters or ulcers.
If no irritation occurs on the skin after the patch test is completed, a second patch test may be administered to screen for more substances. The skin is also examined several days after the initial test results for any delayed reactions.
There are many variables to consider in dermal patch allergy testing, so this diagnostic procedure should always be performed by a licensed dermatologist who can properly administer the test and accurately interpret the results.
What happens next?
After determining what substance is causing the allergy, your dermatologist will provide a treatment plan.
The first step will be to eliminate the allergen causing your reaction. For example, if you are allergic to a fragrance, you will need to find ways to avoid the scent in your household or beauty products or find alternative products.
You may get a formal diagnosis of a skin condition like contact dermatitis or atopic dermatitis (eczema).
Your doctor may give you medication for your rash or other skin issues to help with itchiness, redness and swelling. You will likely be advised to keep an eye on the affected area for signs of improvement. You may have a follow-up appointment to see if eliminating the allergen helped.
Skin allergy patch testing in South Carolina
Dermal patch allergy testing can help you learn about your allergens and what substances to avoid. You do not have to live with itchy skin and unsightly rashes. Schedule a consultation to see if you are a candidate for testing at Columbia Skin Clinic